Electronics deals with the dynamics of electrons. Let us go through some fundamentals of electronics.
Charge
No one knows what really is charge, any more than, it is a physical property of matter that exhibits electrostatic attraction or repulsion in the presence of other charge. It is a conserved quantity; charge cannot be created nor be destroyed. The unit of charge is Coulomb. Like charges repels and unlike charges attracts.
Charge of one electron =1.6x10^ -19
Voltage
Voltage is the electric potential energy per unit charge, measured in joules per coulomb (Volts). Simply it is the potential difference between two points.
Current
It is the rate of charge flow through a conductive medium. unit is Ampere.
I=dQ/dt
Resistance
It is the opposition to the current flow through a conductor. It is the inverse of conductance. Unit is Ohm.
where,
R is the resistance
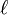 is the length of the conductor
is the length of the conductor
A is the cross sectional area of the conductor
p is the resistivity of the conductor
Frequency
Frequency is a parameter describing the property of a signal. Frequency is defined as the number of cycles per second. It is the inverse of time period of the signal. Unit is Hertz (Hz).
Alternate current (AC)
The direction of current flowing in a circuit is constantly being reversed back and forth. Our (Indian) Domestic electric supply is AC current.
Direct Current (DC)
The electrical current is flowing in only one direction in a circuit. The frequency of DC is zero. Batteries are examples of DC source.
Conductors/Semiconductors/Insulators
An electric conductor is a material that conducts electricity. it's band gap is very small.
Insulators will not allow the flow of electric current through it. The band gap is very large.
Semiconductors acts as insulators at absolute zero but its conductivity increases with increase in temperature. band gap is greater than that of conductors but much less that insulators. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure form semiconductors while extrinsic semiconductors are formed by doping impurities to intrinsic semiconductor for improving the conductivity. Extrinsic semiconductors are of two types; P-type whose majority carriers are holes and N-type whose majority carriers are free electrons.
The band gaps of the above three types of materials are shown below.
`
Please Note:
Most of the pictures i used in this blog are from other sites. If anyone finds any errors or flaws in the contents of the page, please correct me.


